Fiber optic cables and Ethernet cables are both used to transmit data in networking applications, but they differ significantly in terms of their technology, performance, and use cases. Let's explore the differences between fiber optic cables and Ethernet cables:
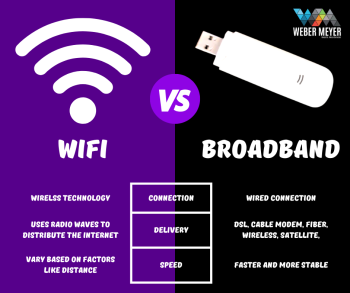
1. Transmission Technology:
- Fiber Optic Cable: Fiber optic cables use light signals to transmit data. They consist of thin strands of glass or plastic (optical fibers) that carry data in the form of pulses of light.
- Ethernet Cable: Ethernet cables, also known as twisted-pair cables, use electrical signals to transmit data. They contain copper wires twisted together in pairs, surrounded by a protective outer jacket.
2. Speed and Bandwidth:
- Fiber Optic Cable: Fiber optics offer much higher data transfer rates and bandwidth compared to traditional Ethernet cables. They can provide speeds ranging from hundreds of megabits per second (Mbps) to several gigabits per second (Gbps) and beyond.
- Ethernet Cable: Ethernet cables have evolved over time, with different categories (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat7, etc.), offering varying data transfer rates. While modern Ethernet cables can handle speeds up to 10 Gbps, they still generally lag behind the potential of fiber optic cables.
3. Distance:
- Fiber Optic Cable: Fiber optics can transmit data over much longer distances without losing signal quality. Single-mode fiber optic cables can span tens of kilometers without the need for signal repeaters.
- Ethernet Cable: Ethernet cables have distance limitations due to signal degradation. Typically, Cat5e and Cat6 cables can handle distances up to 100 meters before experiencing signal loss.
4. Interference and EMI Immunity:
- Fiber Optic Cable: Fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) since they use light signals for transmission. They are ideal for environments with high electromagnetic interference, such as industrial settings or areas with a lot of electronic equipment.
- Ethernet Cable: Ethernet cables, especially unshielded ones, are more susceptible to EMI and can experience performance issues in noisy environments.
5. Installation and Flexibility:
- Fiber Optic Cable: Installing fiber optic cables can be more challenging and requires specialized expertise. They are also relatively fragile, making them less flexible and more susceptible to damage during installation.
- Ethernet Cable: Ethernet cables are easy to install and widely used in both commercial and residential settings. They are more flexible and durable compared to fiber optic cables.
6. Cost:
- Fiber Optic Cable: Historically, fiber optic cables have been more expensive than Ethernet cables, primarily due to the technology involved and the cost of specialized components.
- Ethernet Cable: Ethernet cables are generally more affordable and widely available, especially for shorter distances.
In summary, fiber optic cables are the preferred choice for high-speed, long-distance, and interference-prone networking environments. Ethernet cables, on the other hand, are suitable for most everyday networking needs and are more cost-effective for shorter distances. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the network and the budget available.