Fiber and 5G are two different technologies that serve different purposes when it comes to telecommunications and internet connectivity. They each have their own strengths and weaknesses, and their roles complement each other in building a robust and efficient communication infrastructure.
**Fiber Optic Technology:**
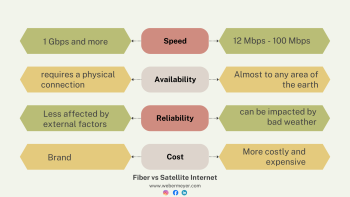
1. **Speed and Capacity:** Fiber optic cables can provide incredibly high data transfer speeds, often reaching up to several gigabits per second (Gbps) and beyond. They have a much higher capacity compared to traditional copper cables, making them ideal for carrying large amounts of data over long distances.
2. **Reliability:** Fiber is not affected by electromagnetic interference and signal loss, which ensures a more stable and reliable connection. This is especially crucial for businesses and critical applications that require constant uptime.
3. **Latency:** Fiber optic connections typically have very low latency, making them well-suited for real-time applications such as online gaming, video conferencing, and financial transactions.
4. **Physical Infrastructure:** Laying fiber optic cables requires significant investment and effort, as it involves digging and installation of physical cables in the ground. This process can be time-consuming and expensive, especially in densely populated urban areas.
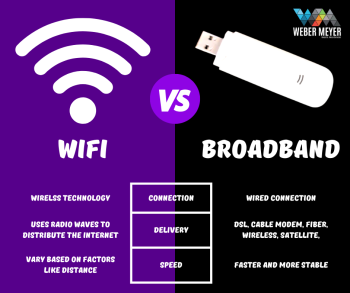
5. **Fixed Connectivity:** Fiber is primarily used for fixed-line connections, providing high-speed internet to homes, offices, and businesses.
**5G Technology:**
1. **Wireless Connectivity:** 5G is the fifth generation of wireless cellular technology. It operates over radio waves and does not require physical cables, making it more flexible and easier to deploy, especially in areas where laying fiber is impractical or costly.
2. **Speed:** 5G promises faster speeds than its predecessors (4G/LTE), and in some cases, it can rival or even exceed the speed of traditional wired connections. However, the actual speed experienced by users can vary depending on factors like network congestion and distance from the cell tower.
3. **Low Latency:** 5G networks aim to reduce latency, making it more responsive for applications that require quick data transmission.
4. **Scalability and Mobility:** 5G is designed to handle a massive number of connected devices simultaneously, making it crucial for the future development of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart cities. It also allows for seamless mobility, supporting devices that are moving at high speeds (e.g., vehicles).
5. **Coverage Challenges:** 5G signals have shorter range compared to 4G and are more easily obstructed by obstacles like buildings and trees. To provide comprehensive coverage, a dense network of small cells is required, which can be costly and time-consuming to deploy.
**Complementary Roles:**
Fiber and 5G are not in direct competition but rather complement each other. They form a part of a diverse communication ecosystem, with each technology being applied where it is most suitable:
1. **Backhaul Connectivity:** Fiber is often used as the backbone infrastructure to carry data from 5G base stations to the core network, ensuring high-speed and reliable connections for the wireless network.
2. **Fixed vs. Mobile Connectivity:** Fiber is ideal for fixed-line broadband connections, offering consistent high-speed internet to homes and businesses. On the other hand, 5G is more suitable for mobile devices and can provide high-speed internet access on the go.
3. **Geographical Considerations:** In urban areas, where the demand for high-speed internet is high and there's existing infrastructure, fiber is a preferred choice. In rural or remote areas, where deploying fiber can be challenging, 5G can be a more feasible option to provide high-speed internet connectivity.
In conclusion, fiber and 5G are both essential technologies that play critical roles in modern communication networks. Fiber excels in delivering ultra-fast, reliable, and stable connections over long distances, while 5G offers wireless mobility and the potential to connect numerous devices simultaneously. Together, they contribute to creating a comprehensive and efficient communication infrastructure for the future.