The terms "fibernet" and "broadband" are often used interchangeably, but it's essential to understand what they mean in the context of internet connectivity.
**Fibernet:**
"Fibernet" is short for fiber optic network, which uses thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as pulses of light. Fiber optic technology provides extremely high data transmission speeds and low latency, making it one of the fastest and most reliable forms of internet connectivity available. It can offer symmetrical upload and download speeds, which means the upload speed is as fast as the download speed. Fiber optic connections are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference and can handle higher bandwidths, making them ideal for heavy internet users, online gaming, streaming, and businesses that require consistent and robust internet access.
**Broadband:**
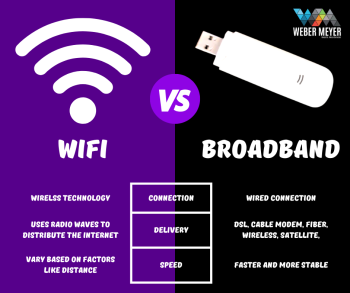
"Broadband" is a term used to describe high-speed internet connections that offer faster data transmission than traditional dial-up connections. Broadband encompasses various technologies, including digital subscriber line (DSL), cable, satellite, and, more recently, fiber optic connections. Each of these broadband technologies has its strengths and limitations, with their speed, reliability, and availability varying based on the location and the infrastructure in place.
**Comparison:**
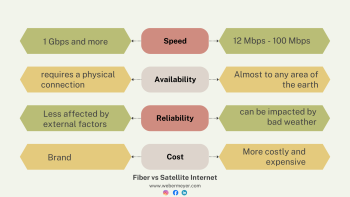
In terms of speed and reliability, fiber optic (fibernet) is generally considered superior to other broadband technologies like DSL and cable. Fiber optic internet can deliver much higher speeds and lower latency, making it ideal for demanding internet activities and households with multiple connected devices.
However, whether fibernet is "better" than broadband depends on the specific context and the user's needs. If a user's location does not have access to fiber optic infrastructure, other broadband options like cable or DSL may be the best available choice. Additionally, some users may not require the absolute highest speeds offered by fibernet and may find other broadband technologies sufficient for their needs.
In conclusion, fibernet, i.e., fiber optic internet, is typically superior to traditional broadband technologies like DSL and cable in terms of speed and reliability. However, the availability and suitability of fibernet vs. broadband depend on the specific location and individual requirements of the user.